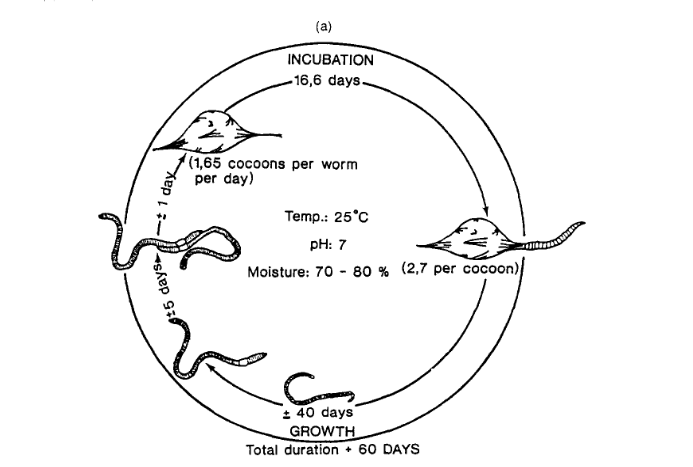
What role do earth worms play in productive soil life?
A great video about the role of earth worms and their gut bacteria on feeding microbes that help fix nitrogen in soils.
What are humans doing to harm Mycology and Earthworm Populations?
- Humans are harming the soil by:
- Watering their lawn with tap water high in cholorine with little to no living microbes.
- Using Round Up to “manage weeds”
- Using Nitrogen only Fertizlers without microbes to “fertilize their lawns.”
“A profound shift in bacterial populationswas observed in all exposed earthworms with Proteobacteria becoming the dominant phylum. Affected bacteria were mostly from the genus Enterobacter, Pantoea and Pseudomonas, which together represented approximately 80 % of the total abundance assigned at the genus level in exposed earthworms, while they were present at a minor abundance (∼1%) in unexposed earthworms.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214750021000627
Glyphosate is the main igredient of Round Up, a Monsanto product. Monsanto is owned by Bayer Chemical Company.
“Our findings indicated reduced species number, density and biomass of earthworms, and increased net carbon mineralization rate in plots with GBH. The plots managed with glyphosate presented a negative effect on the earthworm parameters measured, and we conclude that the earthworms therefore acted as indicators of perturbation. It is also possible that this effect could be due to factors unrelated to the glyphosate that were not considered in this study, such as chemical fertilization or legume litter spatial variability, among others.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0929139313002382
Both Nitrogen only fertilizers without microbes, with salt cystals as the main medium to prevent microbal growth produced by Bayer, as well as Round Up are contributing to the decline of life activity in our soils world wide.
“We found that herbicides significantly decreased root mycorrhization, soil AMF spore biomass, vesicles and propagules. Herbicide application and earthworms increased soil hyphal biomass and tended to reduce soil water infiltration after a simulated heavy rainfall. Herbicide application in interaction with AMF led to slightly heavier but less active earthworms. Leaching of glyphosate after a simulated rainfall was substantial and altered by earthworms and AMF. These sizeable changes provide impetus for more general attention to side-effects of glyphosate-based herbicides on key soil organisms and their associated ecosystem services.”
https://www.nature.com/articles/srep05634?origin=ppub